What Causes Clicking in Back of Head? And What Can You Do About It?
Have you ever had clicking in back of head? Here are some tips and exercises to reduce neck pain, migraines and correct upper and lower spine nerve issues. The anatomical term for the back of the head is the occiput. All the muscles from the top of the spine come up and attach to the occiput. There are fine muscles that go from the back of the head to the very top bone. Unlike most of the vertebrae in the spine which are block-like, they’re rectangular shaped, and then they kind of have a fin coming out the back, that’s called a spinous.
The anatomical term for the back of the head is the occiput. All the muscles from the top of the spine come up and attach to the occiput. There are fine muscles that go from the back of the head to the very top bone. Unlike most of the vertebrae in the spine which are block-like, they’re rectangular shaped, and then they kind of have a fin coming out the back, that’s called a spinous. Then this spinous has muscles attached to it that’s so the segments can be rotated. The down needs pulling from the front but there are muscles attached to the back that pull us back and up. And there are diagonal ones that pull us side to side. So, this is a regular bone of the spine. There are 24 bones of the spine the majority of them are like this, but there are some that are atypical. And the first and second bone in particular are. The first bone is atlas now the skull sits on top of Atlas like in the old mythology. 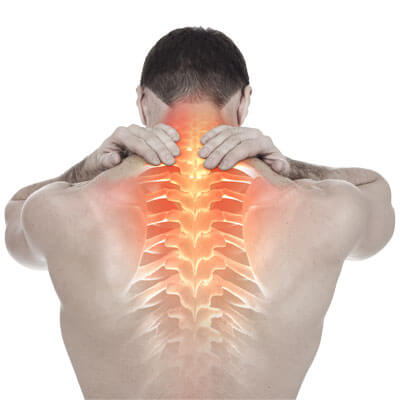 The back of the skull and Atlas, that’s the medical term for the back of the head. Now the clicking in back of the head if there’s been some sort of trauma could have actually been as far back as birth if there’s been pulling when baby comes out or in some cases even when you have the most natural birth in the world when baby comes out there can still be an imbalance. That imbalance can lead to an imbalance in the muscles at the back of the head. There are eight muscles at the back of the head, tiny muscles which are small but have a massive influence on a lot of things. The top ones, the top brown ones – rectus capitus posterior minor muscles, they attach directly to this bone so if they’re in spasm or one side’s in spasm then that’s going to cause this moving surface to be jacked up on one side. So, when we’re moving our heads now there’s possibly audible sounds. Now the audible sound, the clicking is most likely nitrogen gas in the joints in the synovial joints the synovial just means it’s full of fluid so it’s a joint that’s full of fluid and as it’s stretched open the fluid expands but it gets to a point where it can no longer expand, there’s a vacuum form and as the vacuum collapses that’s thought to be the clicking sound that we can hear. Whiplash is another example people have had a few people that have had their hockey sticks around the back of the neck hitting in this kind of area here. That’s very common. Falling off of bicycles, there are thousands of things that can give you this kind of injury. Also trades people, people that are painting the ceiling a lot perhaps they are plasterers and looking up a lot. In that position for prolonged periods of time. But there’s an imbalance in those eight tiny muscles at the back. It can actually radically change what’s happening there. Also, those muscles are controlled by nerves that come out of the spine. So if the top of the spine is out of balance it could distort the signals that go into those muscles okay again if the motion starts to be reduced then the signal going from the motor receptors in the muscles which is feedback to the brain. Now the brain thinks there’s an imbalance and it actually adapts how those muscles are going to contract so again that leads to further imbalance. The brain floats in fluid and at different times it actually dips down, and the brain stem comes down into Atlas so if Atlas and those muscles are out of balance there’s a school of thought that says there’s going to be torsion on the nerve system which in turn is going to start to distort signals.
The back of the skull and Atlas, that’s the medical term for the back of the head. Now the clicking in back of the head if there’s been some sort of trauma could have actually been as far back as birth if there’s been pulling when baby comes out or in some cases even when you have the most natural birth in the world when baby comes out there can still be an imbalance. That imbalance can lead to an imbalance in the muscles at the back of the head. There are eight muscles at the back of the head, tiny muscles which are small but have a massive influence on a lot of things. The top ones, the top brown ones – rectus capitus posterior minor muscles, they attach directly to this bone so if they’re in spasm or one side’s in spasm then that’s going to cause this moving surface to be jacked up on one side. So, when we’re moving our heads now there’s possibly audible sounds. Now the audible sound, the clicking is most likely nitrogen gas in the joints in the synovial joints the synovial just means it’s full of fluid so it’s a joint that’s full of fluid and as it’s stretched open the fluid expands but it gets to a point where it can no longer expand, there’s a vacuum form and as the vacuum collapses that’s thought to be the clicking sound that we can hear. Whiplash is another example people have had a few people that have had their hockey sticks around the back of the neck hitting in this kind of area here. That’s very common. Falling off of bicycles, there are thousands of things that can give you this kind of injury. Also trades people, people that are painting the ceiling a lot perhaps they are plasterers and looking up a lot. In that position for prolonged periods of time. But there’s an imbalance in those eight tiny muscles at the back. It can actually radically change what’s happening there. Also, those muscles are controlled by nerves that come out of the spine. So if the top of the spine is out of balance it could distort the signals that go into those muscles okay again if the motion starts to be reduced then the signal going from the motor receptors in the muscles which is feedback to the brain. Now the brain thinks there’s an imbalance and it actually adapts how those muscles are going to contract so again that leads to further imbalance. The brain floats in fluid and at different times it actually dips down, and the brain stem comes down into Atlas so if Atlas and those muscles are out of balance there’s a school of thought that says there’s going to be torsion on the nerve system which in turn is going to start to distort signals.
Now, what can you do about it?
So, in other words, we want to adjust the spine, take pressure off the nerve system give some relief at that top level for sure. So, adjustments in rhythm that is the secret. The second thing is spinal hygiene exercises so once we unlock the spine you have to be responsible to actually, get the motions in. To improve communication between the brain and the nerves to the muscles in the neck and then the third level.

Nov 11, 2024 at 7:57 AM
I have been diagnosed with FND this causes convolutions in my case to the upper body. This clicking started last week after a severe bout of convolutions . FND is a brain disorder